Here's an illustrative RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) buyer's journey that outlines a general framework to guide the buyer through the stages of awareness, research, evaluation, implementation, and optimisation in their RFID procurement process.
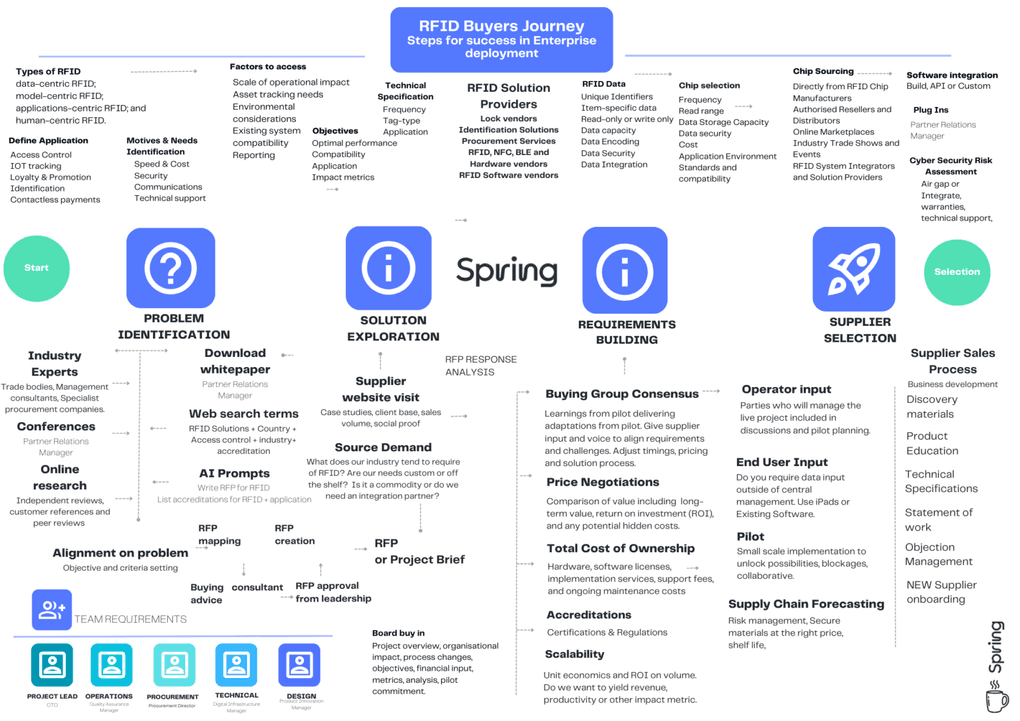
Exploration: Establish the potential benefits and applications of RFID technology. Explore how RFID can improve your business processes, enhance inventory management, or streamline operations.
Actions: Visit trade shows, source via procurement companies, consultancy market leaders, vendor lists on chip manufacturers, technology comparison sites, search engines.
Strategic vision and benchmarks: In this stage, find more in-depth information about RFID technology and its application to your challenge. Compare different RFID systems, vendors, and solutions in the market. Delve into the features, capabilities, and integration options of RFID systems to understand how they align with your specific business needs.
Actions: Define the basics - application identification, RFID form e.g. tag, location, environment, shelf life, lifecycle management, ideal material features, data management, chip requirements.
Solution Design: During this stage, evaluate the specific requirements and objectives. Identify the pain points in their current processes and determine how RFID can address those challenges. Factors such as the scale of operations, chip read range and line-of-sight requirements, integration, environmental considerations, and compatibility with existing systems.
Actions: Assign internal and external responsibilities, gain leadership sponsorship, complete RFP or brief development. Define type of vendor: Lock or door vendors
Identification Solutions, Procurement Services, RFID, NFC, BLE and Hardware vendors, RFID Software vendors
Tools & Vendor Evaluation: In this stage, shortlist potential RFID vendors based on your research and needs assessment. Gather detailed information about each vendor, including their expertise, industry reputation, client testimonials, and case studies. The buyer may reach out to vendors for product demonstrations, consultations, and to request proposals tailored to their requirements.Actions: referrals, online research, statement of work evaluation, samples and demo, pilot at least two options, risk assessment.
Solution Selection: After evaluating vendors, the buyer narrows down their choices and selects the most suitable RFID solution. They consider factors such as system reliability, scalability, ease of integration, implementation support, and lifetime costs. The buyer may also assess the vendor's ability to provide ongoing technical support, training, and system maintenance.
Actions: Regulatory and compliance aligned to your use case and industry, Adoption roadmap, award vendor, assign implementation and activation responsibilities, supply chain, distribution, storage, legal and commercial agreements.
Tip: Semiconductor chip prices change significantly month by month. Consider pre-purchasing or fixing prices on annual quantities prior to vendor selection.
Implementation and Deployment: Once the RFID solution is selected, proceed with the implementation phase. This involves coordinating with the vendor to deploy the RFID system, configure hardware and software components, and integrate it into existing workflows. The buyer may collaborate with internal teams, IT personnel, and vendor representatives to ensure a smooth and successful deployment.
Actions: Interoperability requirements plan, test for data collision, read errors, environmental interference, tag reliability and durability. Write crisis management process, set up contingency workflows.
Training and Adoption: After implementation, the focus on training your team to effectively use the RFID system. They conduct training sessions, workshops, or online tutorials to familiarise employees with RFID technology, best practices, and data management processes. Encourage adoption by highlighting the benefits, demonstrating the system's capabilities, and addressing any concerns or resistance from employees.
Actions: determine roles and KPIs.
Optimisation and Expansion: Once the RFID system is operational, continuously monitor and optimise its performance. They collect data, analyse metrics, and identify areas for improvement. Collaborate with the vendor to fine-tune the system, leverage advanced features, and explore expansion possibilities to other areas of their business.
Download RFID Enterprise Buyers Guide
Download Spring RFID Enterprise Buyers Guide
Ready to enhance your customer experience?
Customise NFC and QR code products for identification, access control and more.